Last updated: October 24, 2024
12 mins read
Overview of the eye
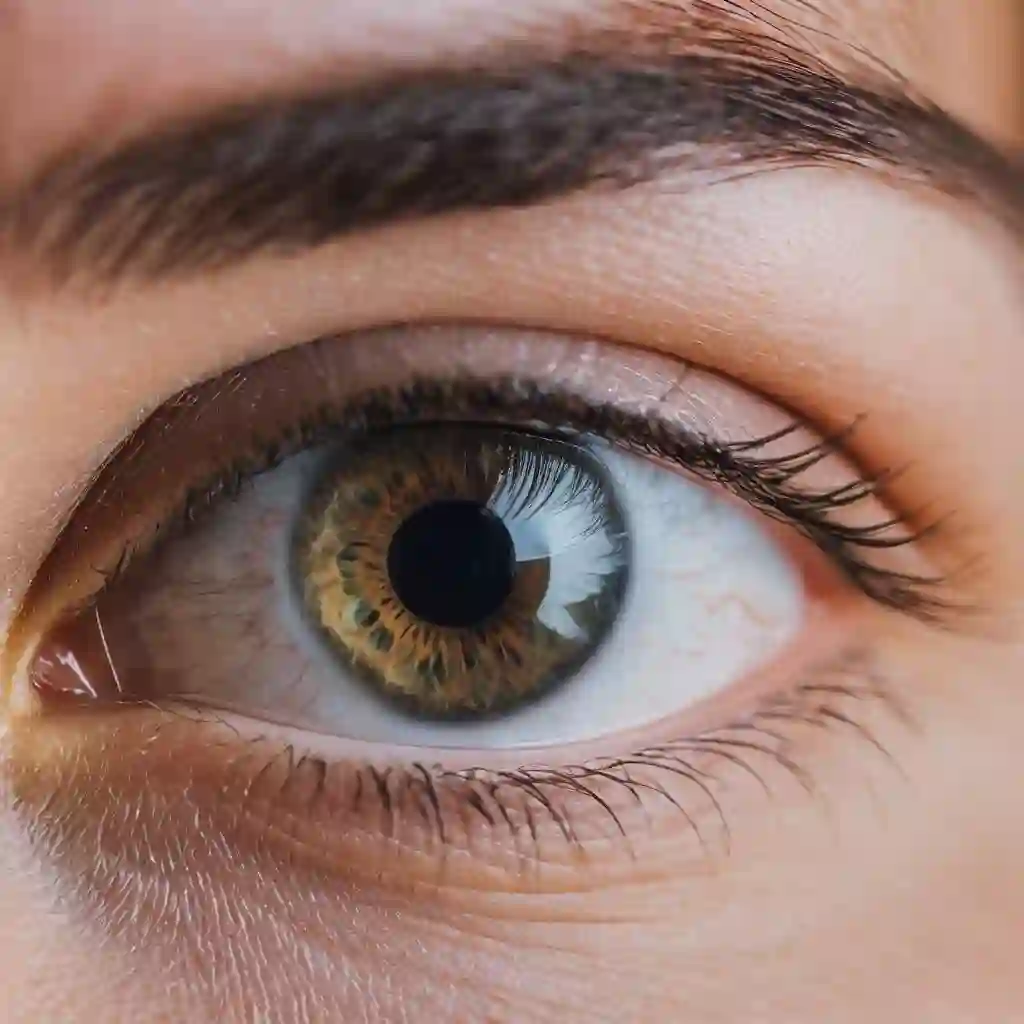
The human eye is the light source for the body. It functions like a camera, which captures images and colors, processes them in harmony with the brain for man to perceive into reality. It's a vital, remarkable and complex structure responsible for vision, detecting light and transmitting visual information to the brain. The eye has over millions of structures working together to create visual information for human. Such structures and a primary components include the cornea, Retina, Lens, optic nerve, iris among many others.
Before you can see and understand what you see (such as the environment, people, water, artifacts, etc.), the eye undergoes several processes before you visualize what you see. This process of vision begins when light enters the eye through the cornea. The light is then focused by the lens onto the retina, where photoreceptors convert it into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve, allowing you to perceive and interpret and understand visual information.
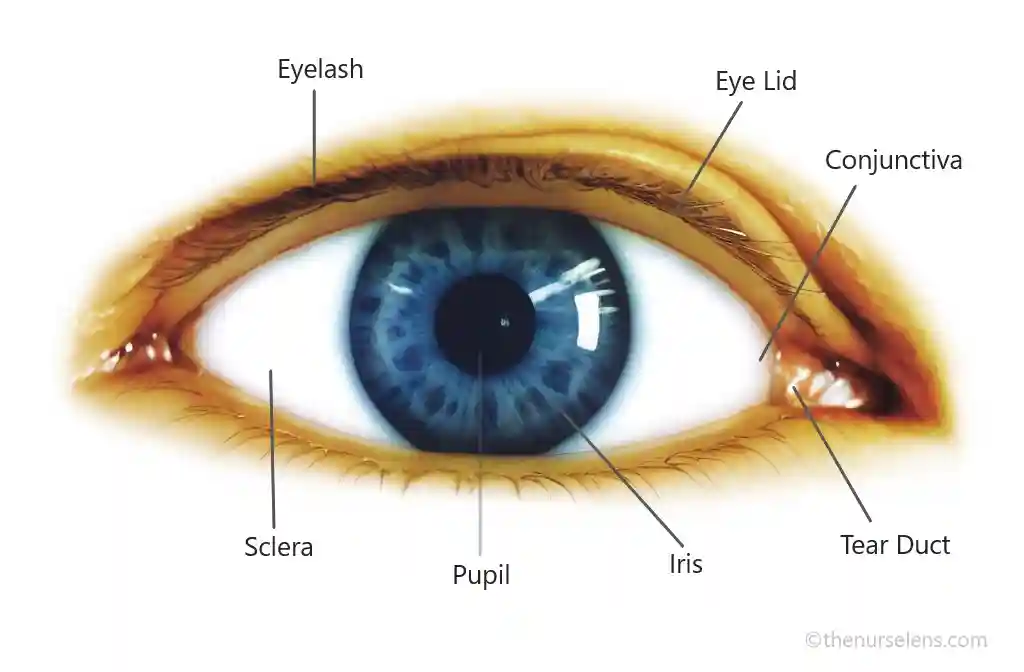
Structures of the Eye
The corneais a transparent outer layer of the eye responsible for allowing light to enter the eye
The Lensis a clear, flexible structure responsible for focusing light onto the retina.
The retinais the innermost layer of the eye containing specialized cells called photoreceptors (Rods and Cons) that converts light received from the lens to electrical signals
The irisis the colored part of the outer layer of the eye. It adjusts the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
The optic nervetransmits electrical signals from the retina to the brain, where they're interpreted as visual information.
The eye performs several vital functions among the basic and the key ones include vision, focusing, color perception, Adaptation and Depth Perception.
advertisement
Functions of the eye
- For Vision:The eye enables sight and perception of the environment.
- Focusing:The eye maintains clear vision by adjusting to varying angles and distances
- Color perception:Photoreceptors distinguishes between different hues and colors.
- Adaptation:Adjustments to different lighting conditions and patterns
- Depth perception:Enables the perception of three-dimensional (3D) vision.
You may also like: What is Pyelitis, causes, signs and symptoms, management & prevention
Eye Care
The eye's intricate structure and functions make it an extraordinary and essential part of the human body which at any given moment, it can also malfunction, as you grow its ability and functions also can deteriorate due to disease and Condition.Prioritizing essential eye health is very important to maintain the eye stability to function properly when also aged.
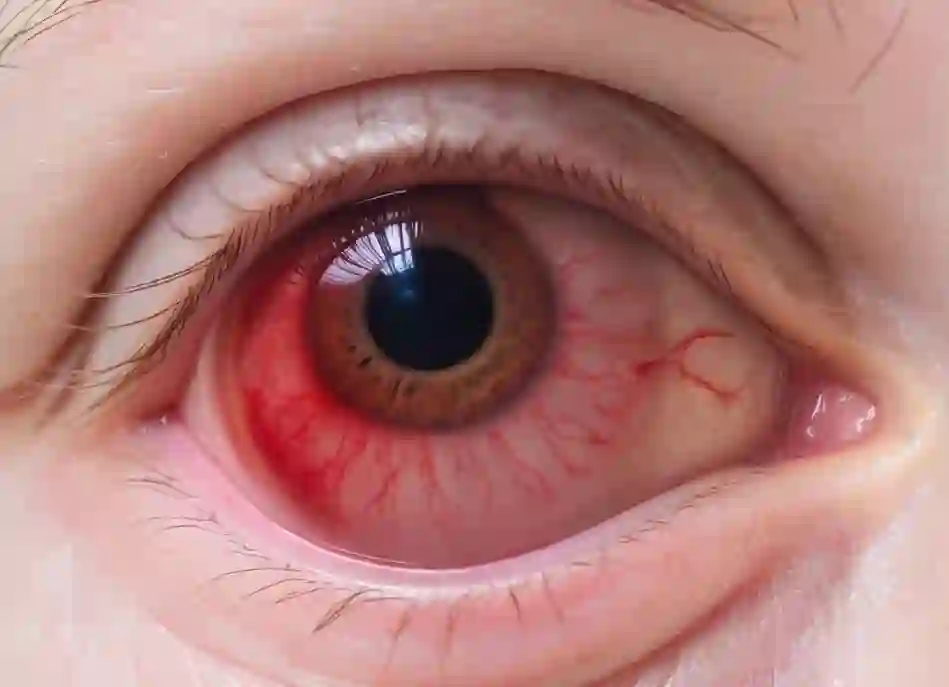
Inflammed conjunctiva
Some Common Diseases and Conditions Affecting the Eye
Cloudiness of the lens of the eye (Cataract)
Increased pressure in the eye (Glaucoma)
Vision loss mostly affects the aged due to problems of the macula (Age-Related Macular Degeneration)
Insufficient tear production of the eye (Dry Eye Syndrome)
Infection of the conjunctiva (Conjunctivitis)
Loss of near vision due to age (Presbyopia)
advertisement
When to consult your Doctor
When you start to experience any of the following changes to your eye, Redness of your eyes that is severe or persistent, vision changes such as blurred or doubled vision, sharp or dull pain to your eyes, when you experience sudden onset of flashes or floaters, discharges that is thick, yellow or green. Immediately see or report to your doctor for early workouts or seek immediate medical attention
Preventive Measures for eye conditions
The focus of prevention is to avoid damaging your eyes, hence you must protect your eyes from potential injuries and harm.
- Regularly visit the hospital for eye check-ups.
- Protect your eye from ultraviolet radiations by wearing Sunglasses with UV protection.
- Ensure to take in Balanced meals. Omega-3 rich foods, vitamins A, C and E promote healthy eye and overall health.
- Avoid or reduce smoking to reduce risk
- Wear goggles to protect your eyes
- Practice screen breaks about every 20 minutes to prevent dryness of the eyes
- Adequate hydration
General Complications of the Eye
There could be Vision loss either Partial or total, Chronic pain, scarring of the eye, Corneal or retinal damage, Anxiety, and also depression if you don't treat your eye condition.
advertisement